Side-Angle-Angle Theorem
The fourth result (theorem) follows from ASA and the fact that the angles of a triangle add to ![]() (which will be proved later using the parallel postulate):
(which will be proved later using the parallel postulate):
SAA
If two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another and a side of the first triangle that is not common to both angles is congruent to a side of the second triangle that is not common to both angles, then the triangles are congruent:
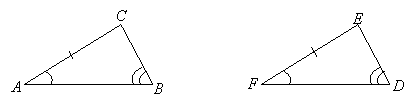
If ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() , it follows by SAA that
, it follows by SAA that ![]() .
.