The Pythagorean Theorem
As we learned in Lesson 4, one of the most important theorems in geometry is the Pythagorean Theorem, named after the Greek mathematician Pythagoras who led in the discovery of its proof around 500 BC. This theorem gives a useful relationship between the three sides of any right triangle, and thus tells how to find a missing side when two of the sides are known.
|
Suppose in
|
|
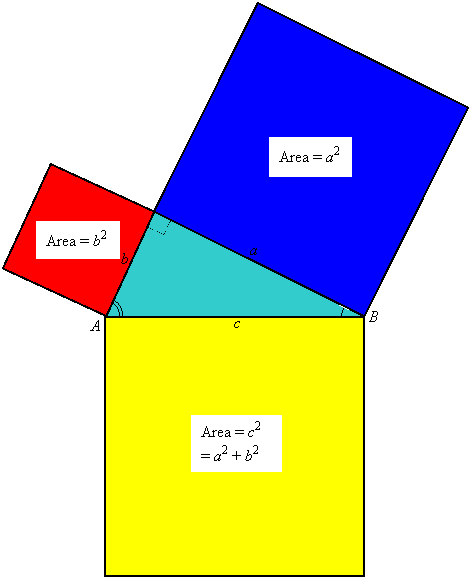
In Pythagoras' time this important theorem was understood in terms of areas. In Unit 1 we learned that if you construct squares on the three sides of a right triangle, then the areas of the two squares on the legs add to the area of the square on the hypotenuse: