A Pythagorean Relation between Sine and Cosine
If ABC is a right triangle with right angle C, then
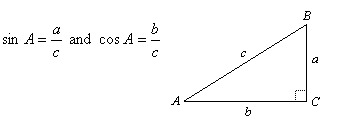 |
If we add the squares of sin A and cos A, we have:
![]()
But a2 + b2 = c2 by the Pythagorean Theorem. Therefore (sin A)2 + (cos A)2 = 1. In other words, the sum of the squares of the sine and cosine of the same angle will equal 1. This is true for any angles (not just acute angles).