Platonic Solids
A Platonic solid is a regular, convex polyhedron. Specifically, the faces of a Platonic solid are congruent regular polygons, with the same number of faces meeting at each vertex. They have the unique property that the faces, edges and angles of each solid are all congruent. There are only 5 regular Platonic solids, named according to the number of faces, the tetrahedron (4 faces), the hexahedron (common cube with 6 faces), the octahedron (8 faces), the dodecahedron (12 faces), and the icosahedron (20 faces):
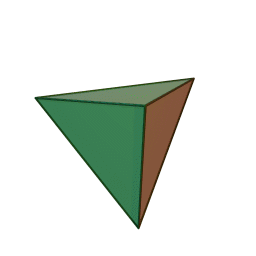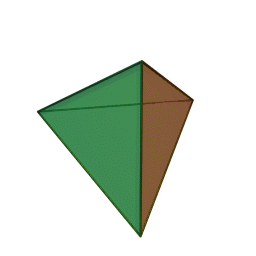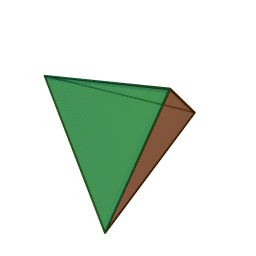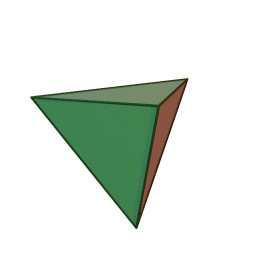
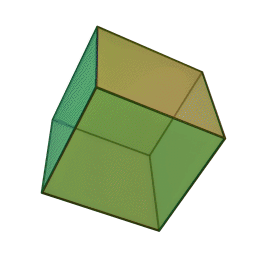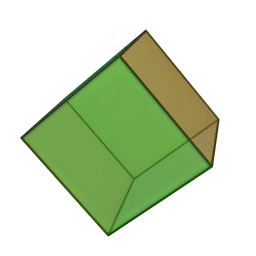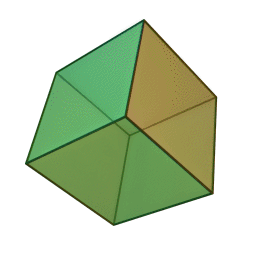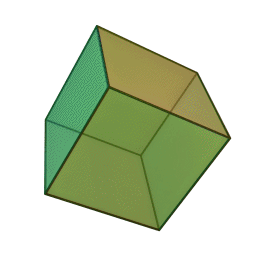
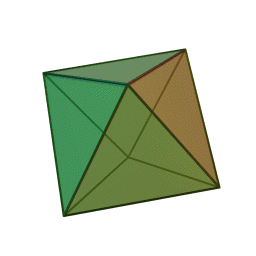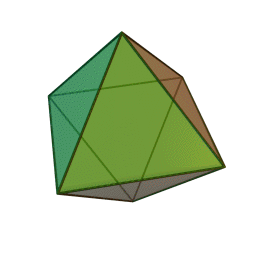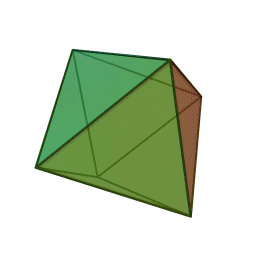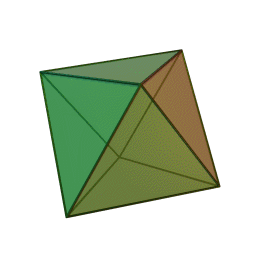
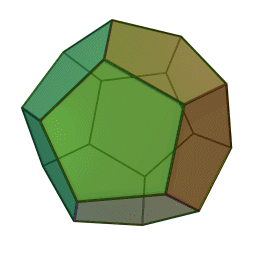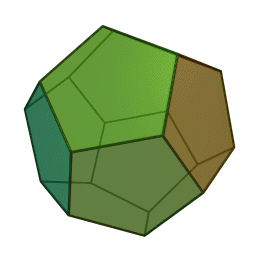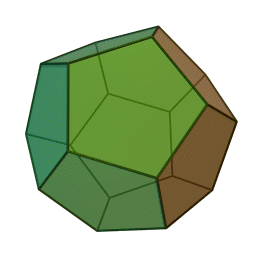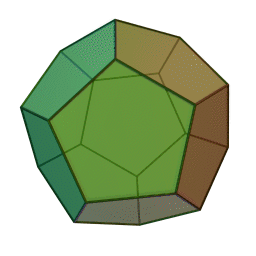
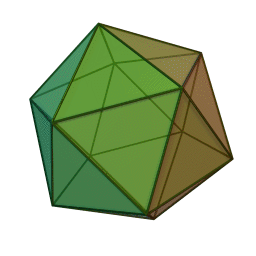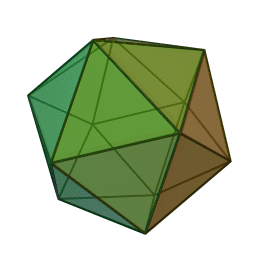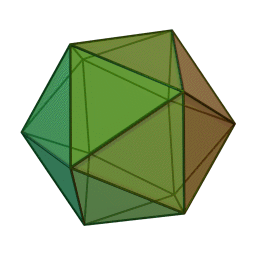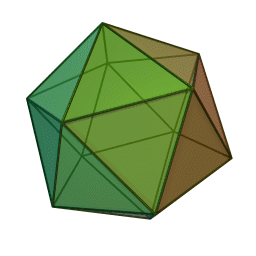
They are named for the ancient Greek philosopher Plato. He wrote about them around 360 B.C. and associated each of the four classical elements (earth, air, water, and fire) with four of these. Earth was associated with the cube, air with the octahedron, water with the icosahedron, and fire with the tetrahedron.
Detailed information about the Platonic solids can be found at the Wikipedia website. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Platonic_solid.